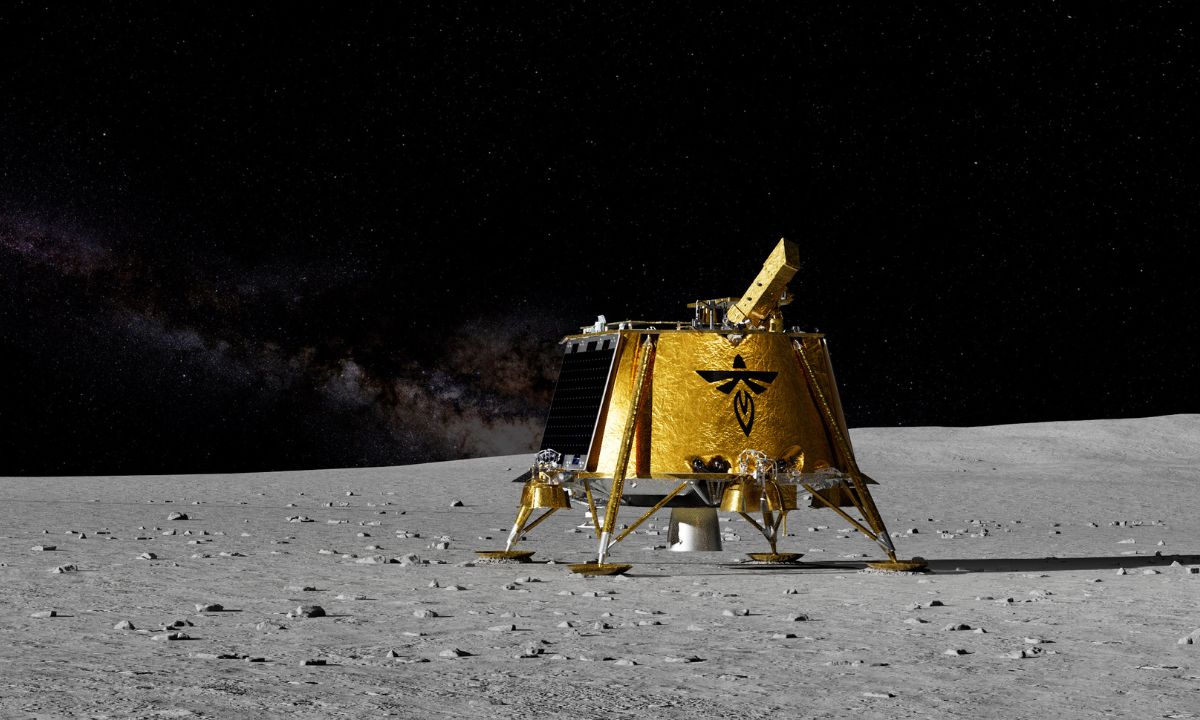
Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost lander has successfully landed on the Moon, marking a significant achievement in private space exploration. This mission, part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program, aims to gather valuable scientific data and support future lunar missions.
The Blue Ghost lander will operate for about 14 Earth days, carrying 10 NASA-sponsored experiments to study the Moon’s surface. Key scientific tools include:
- LISTER – A drill that measures heat flow inside the Moon
- LMS – Sensors to study the Moon’s internal structure
- SCALPSS – Cameras to capture descent and surface images
Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost lander has successfully landed on the Moon, marking a significant achievement in private space exploration. This mission, part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program, aims to gather valuable scientific data and support future lunar missions.
Landing Details
- Date & Time: March 2, 2025, at 3:34 AM EST
- Location: Mare Crisium, a basin on the Moon’s northeastern near side
- Significance: Firefly is the second private company to land on the Moon, after Intuitive Machines’ Odysseus mission in 2024
Scientific Goals and Key Payloads
The Blue Ghost lander will operate for about 14 Earth days, carrying 10 NASA-sponsored experiments to study the Moon’s surface. Key scientific tools include:
SCALPSS – Cameras to capture descent and surface images
LISTER – A drill that measures heat flow inside the Moon
LMS – Sensors to study the Moon’s internal structure
Mission Objectives and Scientific Payloads
The Blue Ghost mission is slated to operate for one lunar day, approximately 14 Earth days, during which it will conduct various scientific experiments. The lander carries ten NASA-sponsored payloads designed to study the Moon’s surface and environment. Key experiments include:
- Lunar Instrumentation for Subsurface Thermal Exploration with Rapidity (LISTER): A drill capable of reaching depths of up to 3 meters to measure the Moon’s internal heat flow, providing insights into its thermal history.
- Lunar Magnetotelluric Sounder (LMS): An instrument deploying electrodes over a 700-square-meter area to measure electrical and magnetic currents, probing the Moon’s interior structure up to depths of 1,000 kilometers. Scientific American
- Stereo Cameras for Lunar Plume-Surface Studies (SCALPSS): A set of six cameras mounted around the base of Blue Ghost to capture imagery during descent and after landing. These images will help researchers produce 3D views of the surface and understand the interaction between the lander’s rocket plume and the lunar soil. nasa.gov
Advancements in Lunar Exploration
The success of Blue Ghost signifies a pivotal advancement in lunar exploration, demonstrating the capabilities of private enterprises to deliver scientific instruments and technology demonstrations to the Moon. This mission contributes to NASA’s Artemis program, which aims to establish a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface by the end of the decade.
Firefly Aerospace’s accomplishment also highlights the increasing collaboration between private companies and government agencies in space exploration. Such partnerships are essential for fostering a sustainable space economy and accelerating technological innovations. The data collected from Blue Ghost’s experiments will inform future missions, including planned endeavors to the Moon’s far side in 2026, as Firefly envisions annual lunar visits with increased frequency over time.
Looking Ahead
As lunar exploration intensifies, the success of missions like Blue Ghost paves the way for more ambitious projects, including crewed missions and the establishment of lunar bases. The information gathered from these missions will enhance our understanding of the Moon’s geology, environment, and potential resources, laying the groundwork for future exploration and utilization.
Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Mission 1 not only demonstrates the feasibility of commercial lunar landings but also signifies a new era in space exploration where private companies play a crucial role in expanding humanity’s reach beyond Earth.